An outline of a strategy to address the commodified housing market. The idea originated from a thought experiment in 2018.
One of the first paradoxical issues surrounding Rent Control (RC) is the difficulty of implementing it, particularly because it would negatively impact the wealthy establishment the most. This often leads to a refusal to even consider the proposal.

This post is a response to a question I didn’t have time to address at the end of a presentation. I discussed the fundamental aspects of the current housing model and explained why unregulated private purchases and rents have become entirely market-driven due to the finalization of the mortgage debt market and the commodification of the living spaces we call home.
The question is an obvious first hurdle to even thinking about an introduction of private RC,
Slightly paraphrased question from my classmate Mark;
“How are you going to get an acceptance from small private landlords let alone institutions”?
My response stems from ideas I’ve been developing for a few years, inspired by a theoretical Beveridge 2.0 report. This includes addressing the “five giants” of a 21st-century neoliberal society in the UK.
It’s very broad, but the main point is how you convince people that the stick of RC will benefit the nervous middle (50-90 percentile) and suspicious asset wealth (top 10%).
Addressing bias
According to behavioural economist Daniel Kahneman, we tend to exhibit a stronger bias toward loss—known as “loss aversion”—than toward gain. This bias significantly influences our decision-making. Initially, it may seem beneficial to be overly cautious, as common sense suggests that careful consideration of financial decisions is wise. However, this tendency can lead to poor judgment in certain situations, as illustrated by gamblers who obsessively chase after their initial losses while ignoring the more rational option of accepting a loss and walking away (Kahneman, 2011). In contrast, an AI algorithm would evaluate the odds and would likely accept the initial loss if it determined that doing so was the best course of action for maximizing long-term gains. Humans, on the other hand, often struggle with this due to the emotional weight of the initial loss, often reacting with the fast thinking, emotion-led reactionary part of our decision-making dual apparatus ( the other being the slow rational side).
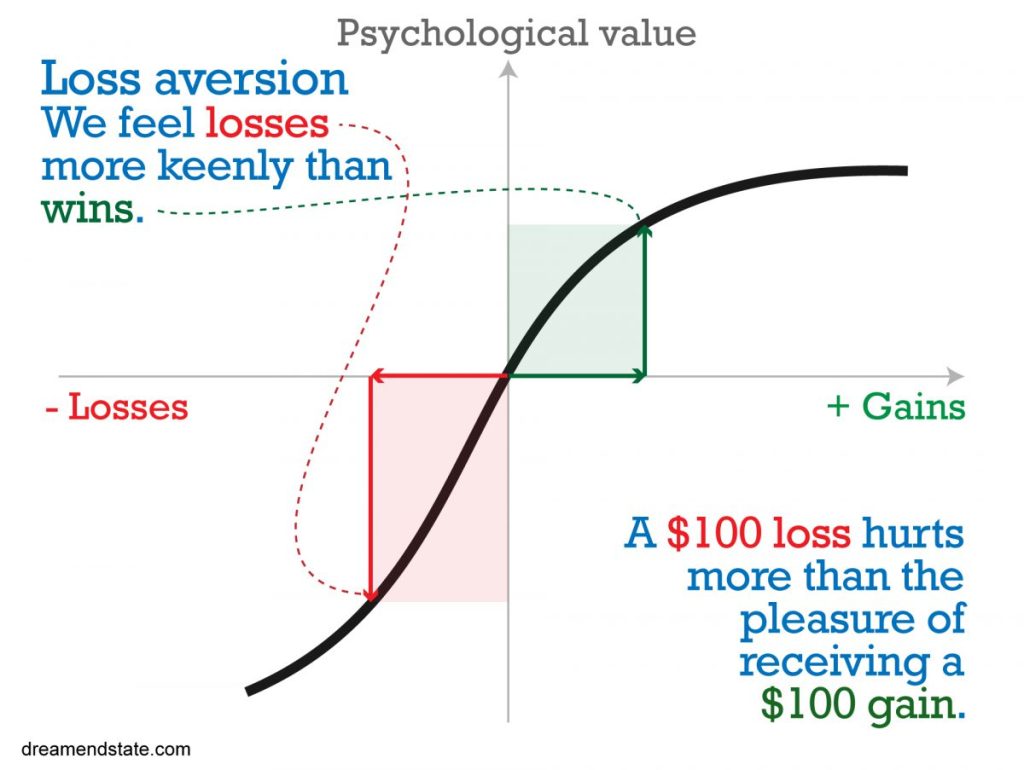
So, with this in mind, to counter the loss, we need a greater gain. Thus, in this report, I figured four carrots to the one stick. This is so important to creating societal jewels (i.e., the NHS) that can be justified to the majority over the small minority of self-seeking short-termists ( and we will see in the paper that all benefit long-term, again, the NHS).
Though it should be stated that any welfare fiscal spending cannot show a direct profit by its very nature, it’s once, twice, thrice removed. The measurement of GDP growth is only seen as a fiscal measurement of ‘production’ ( highlighted as the definition of production has been constantly manipulated; for example, only recently has rentier landlordism been included as a product, even though its extraction, nothing is actually created). The separation of generations cared for, educated from birth to grave, kept healthy, has food, shelter, warmth and no fear of retirement to concentrate on producing measurable wealth during the hours of productive employment.
“Not all can be commodified for direct profit, but what can be produced unhindered by welfare concerns will be measurably more efficient in final output. A sick hungry workforce is absent in mind and body.
